The Main CaseMaster Components
reviewed: 8 February 2025
The CaseMaster framework consists of a number building blocks / modules / components (whichever is the mst appropriate term). Each component will be explained in more detail in the various documents. In this document we briefly introduce you to the CaseMaster landscape.
| Component | Usage |
|---|---|
| Business objects | Define the data entities managed by a CaseMaster application |
| Expressions | Representation of a value; can be a simple literal or a complex expression |
Casemaster script (.cms) |
Scripting language to implement flow control (if-then-else, do-while, etc) |
| Pages | Online web pages |
| Services | Web services (for example API's) |
| Processes | Background processes |
| Documents | Document templates |
| Scripts | Helper scripts |
| Web runtime | Runtime engine to host pages and services |
| Process runtime | Runtime engine to host processes |
| Admin tools | Various utilities to manage CaseMaster applications |
| Dev tools | Various utilities to help with CaseMaster development |
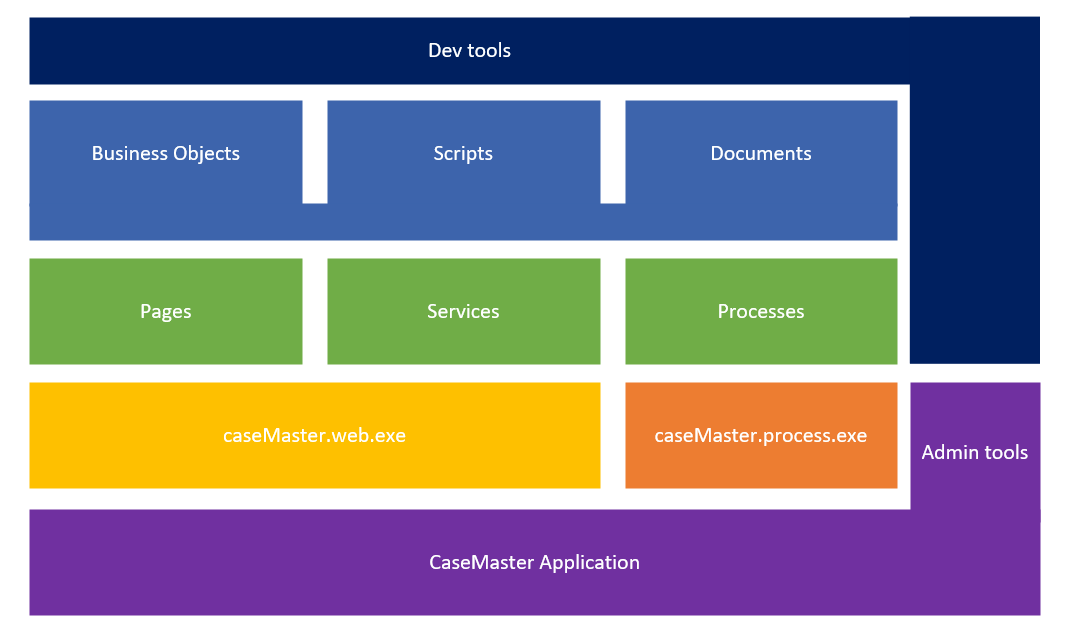
- End-user Application
- The end goal of all CaseMaster development is obviously to develop end-user applications
- Part of each application are the web- and process runtime environments
- A suite of admin tools help power users and application administrators to keep a CaseMaster application up & running
- The two runtime environment will use page, service and process scripts that directly make up the features of the application
- The pages, services and processes in turn will use business objects, scripts and documents
- Developers will use a suite of development tools to be productive
Business Objects
Business objects descrive the data managed by a CaseMaster application. A key concept of CaseMaster is to describe data in great detail in a standard way and link these self describing business objects to a large library of routines that can work with these descriptors; a library of business object savvy components.
This may sound abstract right now but is an essential concept of CaseMaster and is a key factor to the rapid development that CaseMaster enables.
Expressions
Expressions can best be compared to the value in an Excel cell. They can be simple literals (e.g. 1, 5/3/1966 or 'Bertus Dispa') or complex functions that evaluate to a value (e.g. today() or random( 1, 6)).
CaseMaster Script (.cms)
Expressions are powerful but have their limitations. Back to our Excel analogy. We all know how a complex Excel function can get out of hand quickly and is hard to understand and maintain. Advanced Excel users can extend the power of Excel using VBA scripting.
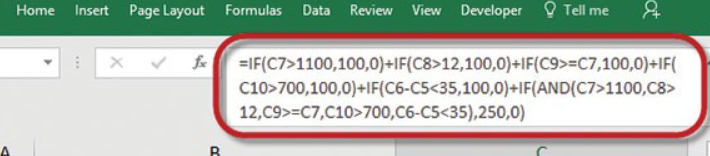
In a similar way, in CaseMaster you can move from expressions to CaseMaster scripting; a powerful programming language that allow you to overcome the limitations of expressions. CaseMaster Script is often referred to as cms as this is the extension of CaseMaster Script files.
Pages
Pages are specific .cms files that implement web pages and are used to build the online features of the CaseMaster applications.
Services
Services are specific .cms file that implement web services. Web service use the same technology that lives under the hood of web browsers but are designed for system-to-system instead of user-to-system communication.
Processes
Processes are specific .cms file that are running under the control of the Process runtime environment. These are known background processes and run without any uiser intervention. Examples of processes are:
- Send payment reminders every Friday at 17:00
- Generate documents, save as PDF and email as attachments in the background
Documents
Documents are specific .cms files used to generate documents which are based on Microsoft .doc / .docx or OpenOffice .docx templates.
Documents can be used by pages, services and processes but do not run directly under the control of the web or process runtime environments
Scripts
Scripts are .cms files with helper functions that can be used by pages, services and processes but do not run directly under the control of the web or process runtime environments.
Web Runtime Environment
The web runtime environment is installed on a server and hosts pages and services.
Process Runtime Environment
The web runtime environment is installed on a server and hosts processes.
Admin Tools
A suite of tools designed to enable power users and application administrators to manage a CaseMaster application. Examples:
- Maintain user profiles
- Deal with application log files
- Monitor page usage and performance
- ...
Dev Tools
A suite of development tools designed to boost productivity of CaseMaster developers. Examples:
- VSCode extension to provide CaseMaster intellisense and code completion
- Data dictionary browser
- SQL generator based on business object definitions
- ...