# Quick Search and Entity Size
reviewed: 9 March 2025
Quick Search in Action
Quick search is another CaseMaster feature designed to bring a lot of functionality to the ens-user without costing the developer and headaches.
There are two prominent places in CaseMaster systems where the quick search shines:
- The so called quick search list
- Searching on drop-downs based on foreign keys
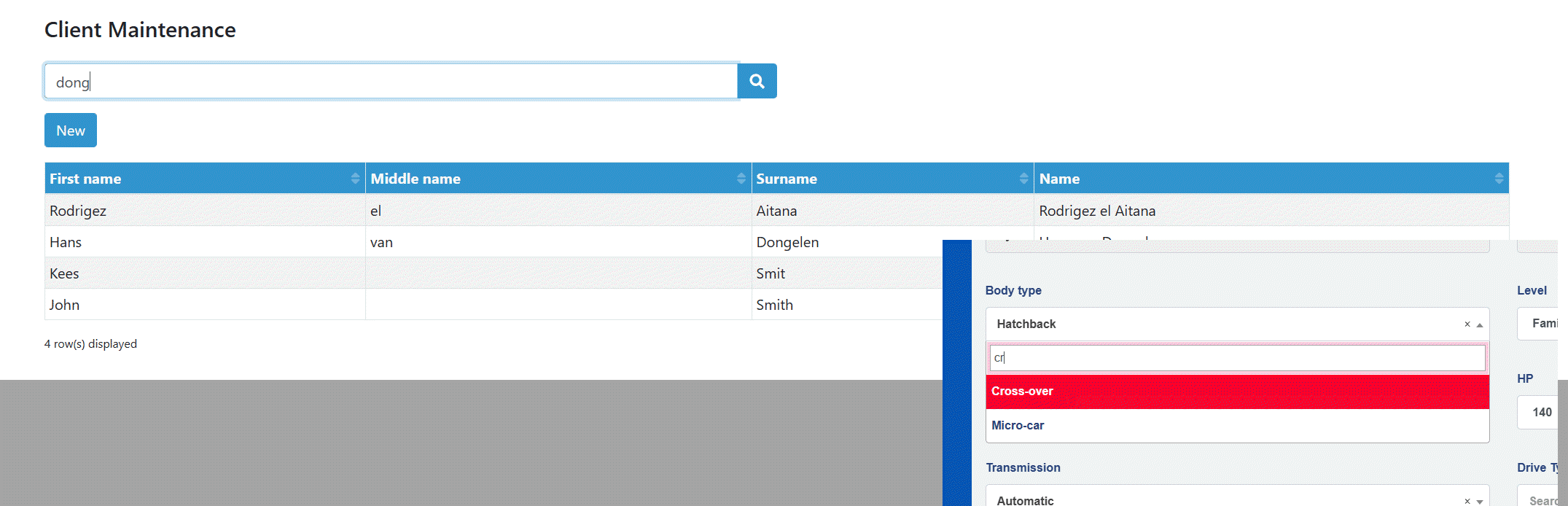
In its simplest form, the quick search will apply the filter value (dong or cr in the examples from the screenshot) and turn this into a where clause based on the attributes that are included in the quick search.
For example, assume that the client entity has the attributes name, email and telephone included in the search attribute group. The quick search from the example above would translate to the following SQL:
"client"."name" LIKE 'dong'
OR "client"."email" LIKE 'dong'
OR "client"."telephone" LIKE 'dong'
Quick Search Syntax
The quick search comes in three variations:
- Simple
- Filter
- Where
Simple Modus
We have already seen the simple option in action. This is the default behaviour. The quick search filter value is taken as a string and is used to construct a SQL where clause based on the attributes included in the quick search.
Filter Modus
You can also start the quick search with the reserved prefix filter:. This will trigger the filter modus. You can now combine multiple search terms with the reserved tokens. The reserved tokens are:
| Token | Usage |
|---|---|
& |
AND: filter where both a and b match |
\| |
OR: filter where either a or b match |
( ) |
Precedence: force sequence of evaluation |
= |
Exact equal (as opposed to starts with or contains) |
!= |
Not equal |
! |
Does not start with or does not contain |
\ |
Escape next character of its special meaning |
The filter option is best explained by a number of examples. These examples are based on a table with the following id's, names and towns:
| id | Name | Town |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Smith | Mansfield |
| 2 | Jones | Nottingham |
| 3 | Charles | Melton Mobray |
| 4 | King | Leicester |
| 5 | Brown | Nottingham |
| 6 | Black | Leicester |
| 7 | White | Melton Mobray |
| 8 | Smith | Melton On Trent |
| 9 | Smyth | Melton Mobray |
Check out the following example:
| Example | Returns | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| smith | 1, 8 | When name is not marked as a soundex attribute |
| smith | 1, 8, 9 | When name has been marked as a soundex attribute |
| filter:smith & melton | 8 | |
| filter:smith | melton | 1, 3, 7, 8, 9 | |
| filter:smith | ( melton & mobray ) | 1, 3, 7, 9 | |
| filter:smith & mans | 1 | |
| filter:smith & =mans | - | Nothing matches man exactly |
| filter:smith & !mans | 8 |
Where Clause Modus
The final modus is the where clause modus. This is intended for developers and trained power users only. The where clause modus is triggered by the reserved prefix where:. What follows i interpreted as a Casemaster where clause.
where:id>2 & cmCreatedBy={ user() } & #is('active')
Considerations and EntitySize
There are a couple of details that are taken into consideration:
- You can include non-string fields in the quick search group. However, these will only be included in the search of the search-phrase has the correct type (e.g the search phrase
hellowill have numeric attributes excluded from the quick search) - Quick search will use starts-with or contains for strings (unless you use
filter:and explicitly force equals / not equals). See also the paragraph on entity size
We have seen that we can assign an entity size top an entity (see here). The default entity size is small. The values are size: entitySize.Small, entitySize.Medium or entitySize.Large.
The entity size is intended as a hint to the number of rows in the associated table. It acts as a hint to CaseMaster on how to generate certain SQL. The actual number of rows depends on many factors such as the RDBMS, the number of users, etc. Typically, in a professional server environment medium starts at a several hundreds of rows and large at several thousands.
// Other stuff here
table: 'client'
sequence: 'client'
primaryKey: 'id'
deleteRule: deleteRule.PerRelation
auditable: auditing.Auditable
size: entitySize.Large
// Other stuff here
For the quick search feature, the entity size has the following consequence:
| Size | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Small | Use contains for string attributes |
| Medium | Use contains for string attributes |
| Large | Use starts-with instead of contains |
Using Quick Search in Where Clauses: #qsearch()
You can include quick search into a where clause using the #qsearch() function.
bo.count( 'client', '#qsearch( name, "acme" )' )
<End of document>